- Home
- About us
About LHD Law Firm
Vietnam is one of the fastest-growing economies in the world. The low cost of living and highly qualified population make it an ideal location for foreign companies who are looking to branch out and invest. However, expanding internationally has its disadvantages as well. Not knowing the local laws and regulations makes it a thousand times harder to open a company overseas.
- Locations
- Practices
- News & insights
Newsroom
Lastest news







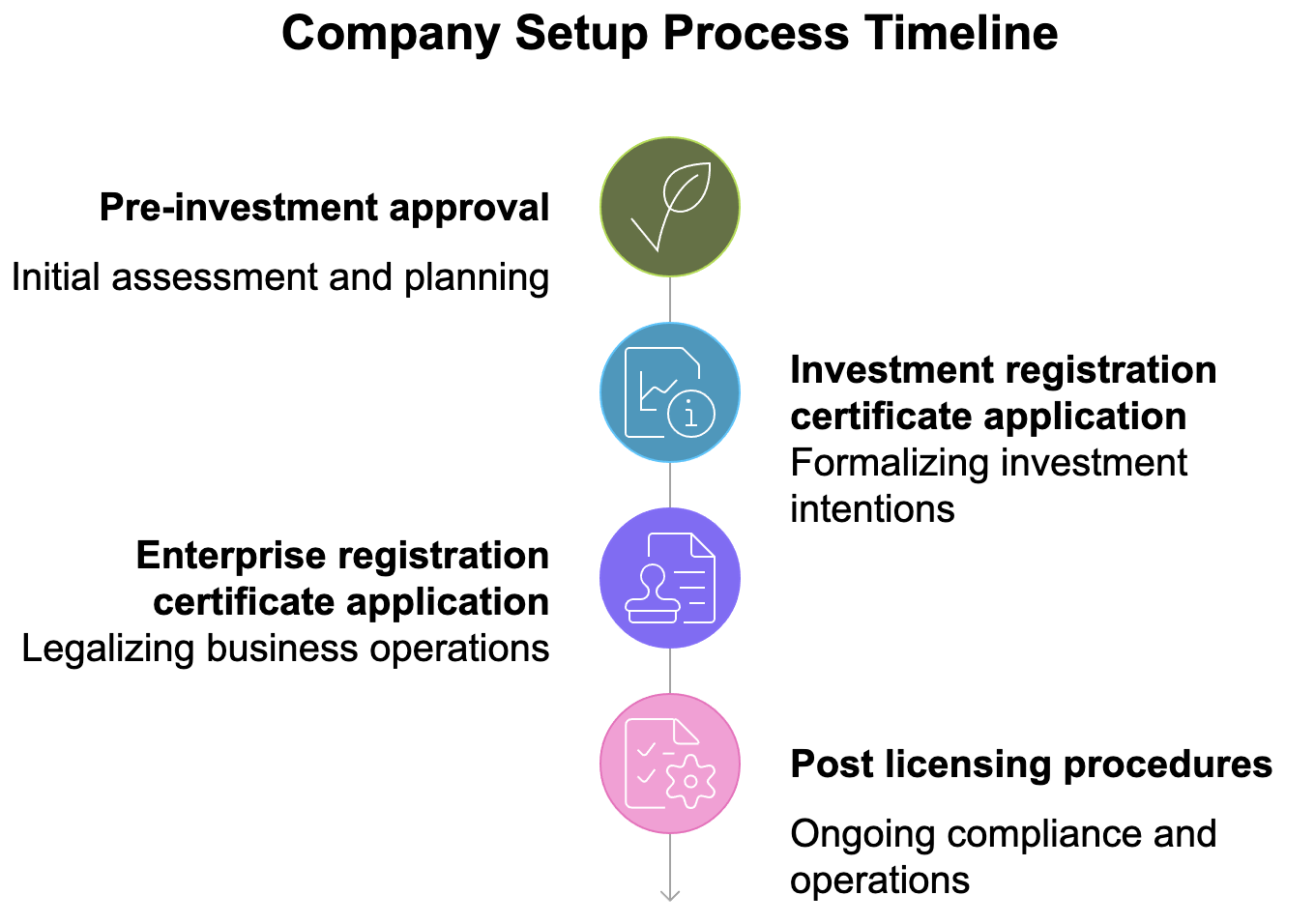




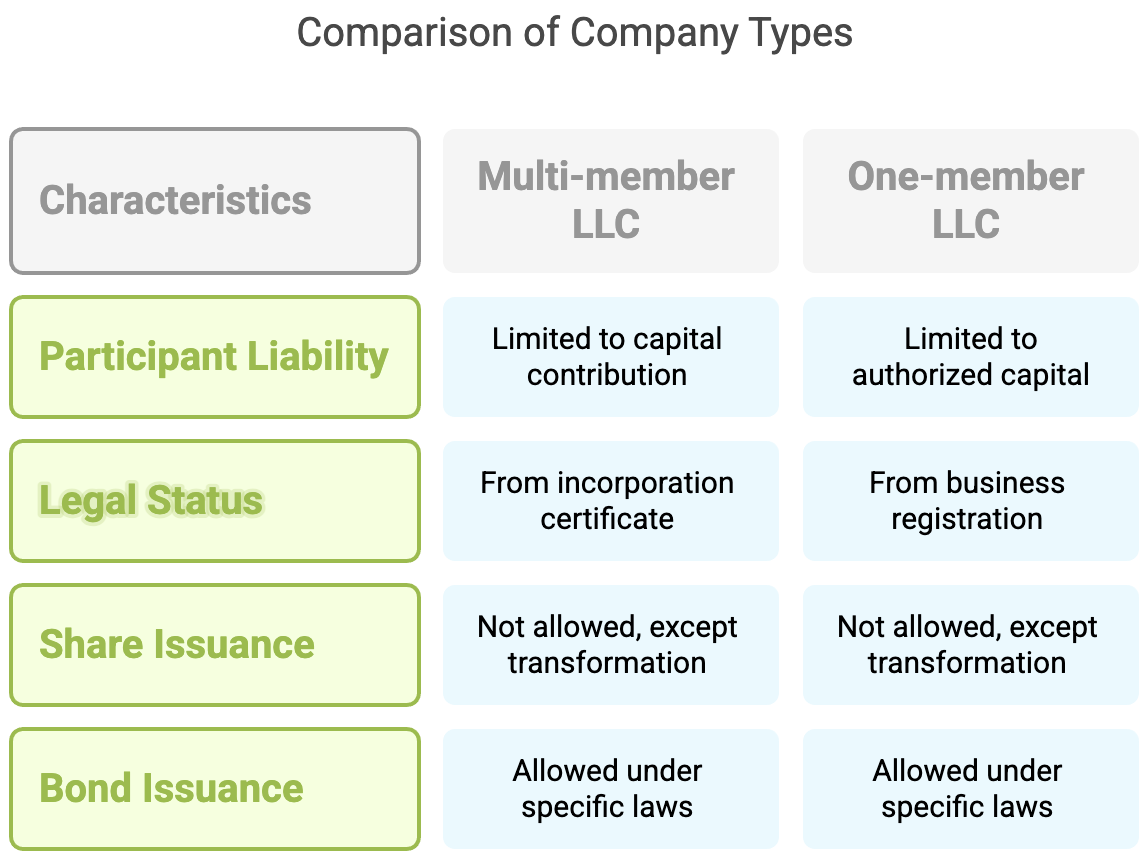








![REGISTER COMPANY IN VIETNAM AS A FOREIGNERS [BEST ADVICE]](/data/News/tips-of-set-up-company-in-vietnam-lhd_1715582789.png)












Comment
Dear LHD Law Firm Ellip Capital is interested in Setting up a company in Vietnam to do Business and investment in the financial sector. Request you to please guide us as to the legal framework and the cost of setting up the company.The cost should also include rentals for office and any other hidden cost. Regards,
Hi LHD Law Firm After looking your company website www.en.luathongduc.com we lookup and read content - Our company is now looking at setting importing and distribution of the food supplements products (Vitamins) 100% FDI. We will import the food supplements products to Vietnam and do distribution locally. Please kindly advise us on the cost of setting up the company and any license requirements. Regards
Can foreigners start a business in Ho Chi Minh?, can they open a bar or coffee shop/restaurant in HCM ? Alex J